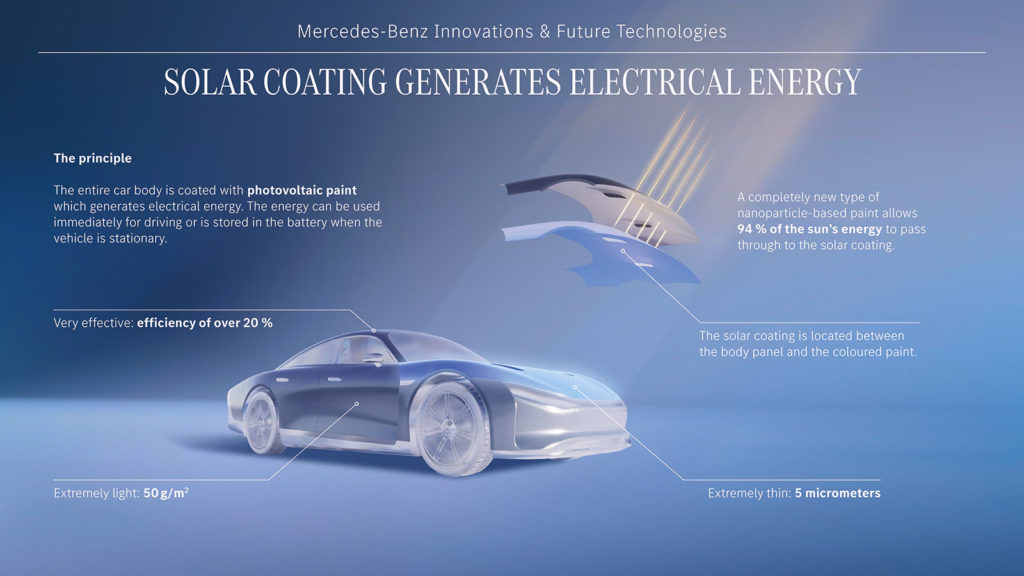
(PR) Mercedes-Benz is researching a new type of solar modules that could be seamlessly applied to the bodywork of electric vehicles – similar to a wafer-thin layer of paste. At 5 micrometers thin, these are significantly thinner than a human hair, weigh just 50 grams per square meter and are packed full of energy. The active photovoltaic surface can be applied to any substrate. The solar cells have a high efficiency of 20 percent. An area of 118.4 square feet (equivalent to the surface of a mid-size SUV) could produce energy for up to 7,456 miles per year under ideal conditions. The energy generated by the solar cells is used for driving or fed directly into the high-voltage battery. The photovoltaic system is permanently active and also generates energy when the vehicle is switched off. In the future, this could be a highly effective solution for increased electric range and fewer charging stops.
The amount of energy produced depends on levels of shade, intensity of the sun and geographical location. Mercedes-Benz drivers in Stuttgart, Germany drive an average of 32 miles per day. Around 62 percent of this distance would be covered using solar energy. In Los Angeles, there is even a surplus of solar energy. It could be used for 100 percent of their driving, on average, and the surplus of energy could be fed directly into the home network via bidirectional charging.
Solar paint has a high level of efficiency and contains no rare earths or silicon – only non-toxic, readily available raw materials. It is easy to recycle and considerably cheaper to produce than conventional solar modules. The Mercedes-Benz research department is currently working to enable use of the new solar paint on all exterior vehicle surfaces – regardless of shape or angle.