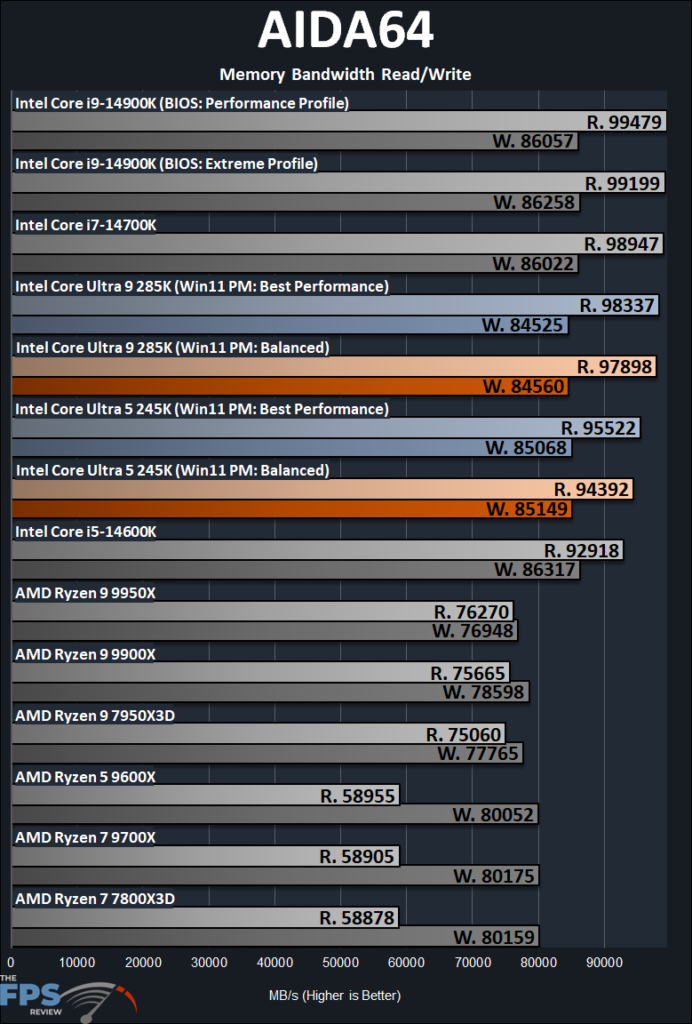
AIDA64 Memory Bandwidth & AES
Now we will look at some specific AIDA64 CPU Benchmarks that test specific parts of the CPUs. The AIDA64 AES benchmark measures CPU performance using AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) data encryption. In cryptography, AES is a symmetric-key encryption standard. AES is used in several compression tools today, like 7z, RAR, and WinZip, and also in disk encryption solutions like BitLocker.
We will also look at Memory Bandwidth. The LGA1700 and LGA1851 platforms (Raptor Lake and Arrow Lake) are using identical memory, set at XMP 1 timings of CL34 and 6400MT/s in Gear 2. The AMD AM5 platform is running at EXPO 1 timings of CL32 at 6000MT/s.
In terms of memory bandwidth, the important factor here is that the Raptor Lake-R and Arrow Lake-S CPUs are running with the same memory configuration, timings, and MT/s. Therefore, we find that memory bandwidth is rather similar, but interestingly a little bit lower on the new LGA1851 Arrow Lake platform.
We do see about a 1,100MB/s read difference (1%) between the Intel Core Ultra 9 285K and the Intel Core i9-14900K. On the write performance there’s a more significant 1,500MB/s (2%) bandwidth difference. The Intel Core Ultra 5 245K, however, is a bit faster than the 14600K on read bandwidth, but a bit slower on write performance, but not a large degree. You can’t really compare this to the AMD configuration, they are completely different architectures, memory controllers, and of course different DDR5 speeds. We do see in terms of raw bandwidth, Arrow Lake (similar to Raptor Lake) has about 28% more raw bandwidth on read and a closer 10% difference on write bandwidth.
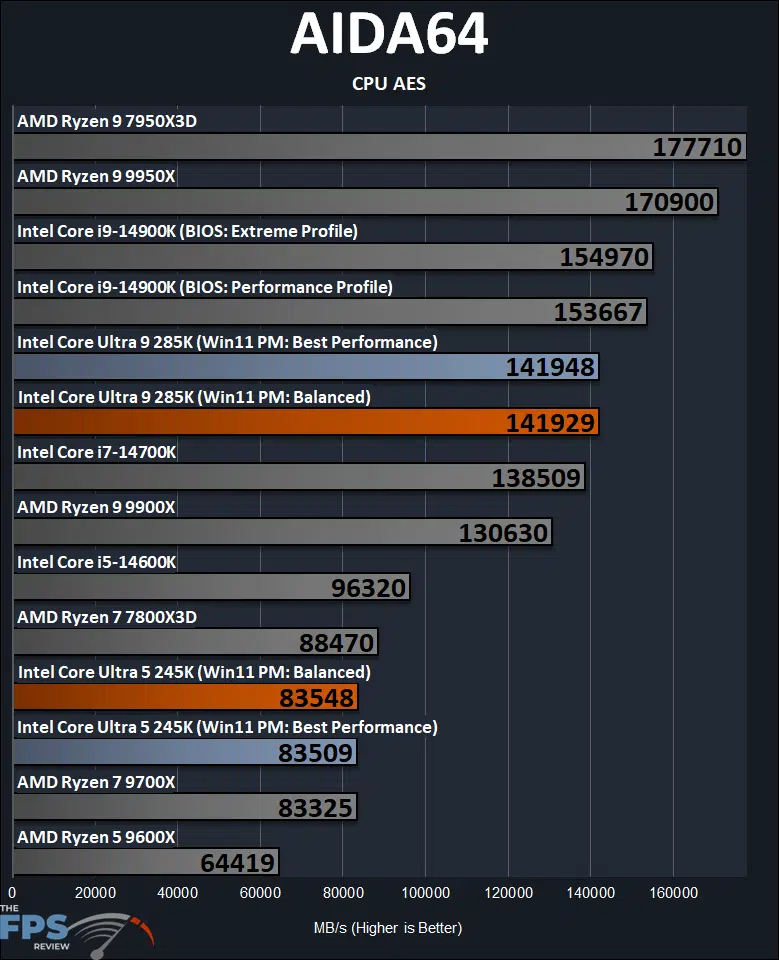
The CPU AES benchmark is good for showing multi-core performance, as well as cache performance, as we can see the 7950X3D and 7800X3D doing quite more than usual, thanks to their larger L3 cache. Because this is a more multi-core focused test, we also don’t see much difference between “Balanced” or “Best Performance” power profile modes on the Intel Core Ultra 9 285K or Ultra 5 245K.
In terms of performance, the new Intel Core Ultra 9 285K ends up being 8% slower than the previous generation Intel Core i9-14900K. Compared to the competition, the 285K ends up being 17% slower than the AMD Ryzen 9 9950X. The Intel Core Ultra 5 245K ends up being 13% slower than the previous generation Intel Core i5-14600K, and just on par or parity with the AMD Ryzen 7 9700X.